Cardiff Castle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cardiff Castle ( cy, Castell Caerdydd) is a
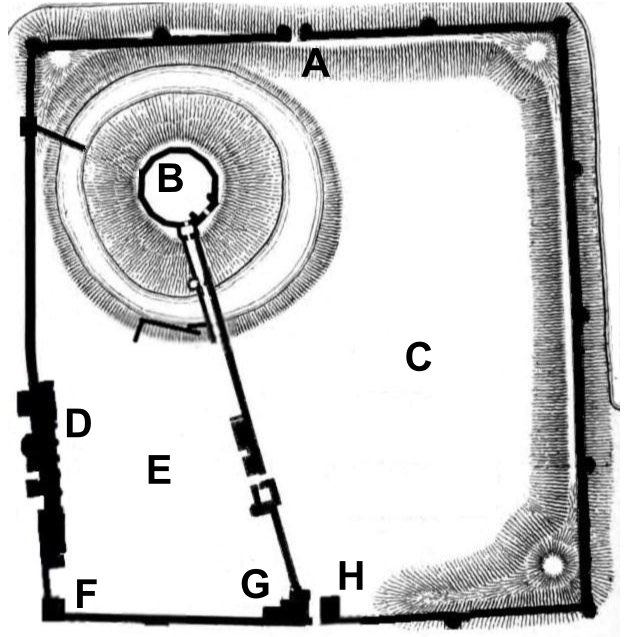 The
The
 Upon Isabel's death in 1217 the castle passed through her sister to Gilbert de Clare, becoming part of the
Upon Isabel's death in 1217 the castle passed through her sister to Gilbert de Clare, becoming part of the
 By the 15th century, the Despensers were increasingly using Caerphilly Castle as their main residence in the region rather than Cardiff. Thomas le Despenser was executed in 1400 on charges of conspiring against Henry IV. In 1401 rebellion broke out in North Wales under the leadership of
By the 15th century, the Despensers were increasingly using Caerphilly Castle as their main residence in the region rather than Cardiff. Thomas le Despenser was executed in 1400 on charges of conspiring against Henry IV. In 1401 rebellion broke out in North Wales under the leadership of  Cardiff Castle remained in the hands of Richard's son,
Cardiff Castle remained in the hands of Richard's son,
 In 1610 the
In 1610 the  Lady Charlotte Herbert was the last of the family to control Cardiff Castle. She married twice, latterly to Thomas, Viscount Windsor, and on her death in 1733 the castle passed to their son,
Lady Charlotte Herbert was the last of the family to control Cardiff Castle. She married twice, latterly to Thomas, Viscount Windsor, and on her death in 1733 the castle passed to their son,
 Work began on Lord Bute's coming of age in 1868 with the construction of the high Clock Tower. The tower, built in Burges's signature
Work began on Lord Bute's coming of age in 1868 with the construction of the high Clock Tower. The tower, built in Burges's signature  The central part of the castle comprised a two-storey banqueting hall, with the library below. Both are enormous, the latter to hold part of the bibliophile Marquess's vast library. Both included elaborate carvings and fireplaces, those in the banqueting hall depicting the castle itself in the time of Robert, Duke of Normandy. The decoration here is less impressive than elsewhere in the castle, as much of it was completed after Burges's death by Lonsdale, a less talented painter. The Arab Room in the Herbert Tower remains however one of Burges's masterpieces. Its jelly mould ceiling in a Moorish style is particularly notable. It was this room on which Burges was working when he died and Bute placed Burges's initials, and his own, and the date 1881 in the fireplace as a memorial. The central portion of the castle also included the Grand Staircase, recorded in a watercolour perspective prepared by
The central part of the castle comprised a two-storey banqueting hall, with the library below. Both are enormous, the latter to hold part of the bibliophile Marquess's vast library. Both included elaborate carvings and fireplaces, those in the banqueting hall depicting the castle itself in the time of Robert, Duke of Normandy. The decoration here is less impressive than elsewhere in the castle, as much of it was completed after Burges's death by Lonsdale, a less talented painter. The Arab Room in the Herbert Tower remains however one of Burges's masterpieces. Its jelly mould ceiling in a Moorish style is particularly notable. It was this room on which Burges was working when he died and Bute placed Burges's initials, and his own, and the date 1881 in the fireplace as a memorial. The central portion of the castle also included the Grand Staircase, recorded in a watercolour perspective prepared by

Cardiff Castle's official websiteFilm footage of the 1947 handover ceremony
{{Authority control Economy of Cardiff Castles in Cardiff Grade I listed buildings in Cardiff Grade I listed castles in Wales Mock castles in Wales
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
castle and Victorian Gothic revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
mansion
A mansion is a large dwelling house. The word itself derives through Old French from the Latin word ''mansio'' "dwelling", an abstract noun derived from the verb ''manere'' "to dwell". The English word '' manse'' originally defined a property l ...
located in the city centre of Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingd ...
, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
. The original motte and bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or Bailey (castle), bailey, surrounded by a protective Rampart (fortification ...
castle was built in the late 11th century by Norman invaders on top of a 3rd-century Roman fort. The castle was commissioned either by William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Norman ...
or by Robert Fitzhamon
Robert Fitzhamon (died March 1107), or Robert FitzHamon (literally, 'Robert, son of Hamon'), Seigneur de Creully in the Calvados region and Torigny in the Manche region of Normandy, was the first Norman feudal baron of Gloucester and the Nor ...
, and formed the heart of the medieval town of Cardiff and the Marcher Lord
A Marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A Marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in F ...
territory of Glamorgan
, HQ = Cardiff
, Government = Glamorgan County Council (1889–1974)
, Origin=
, Code = GLA
, CodeName = Chapman code
, Replace =
* West Glamorgan
* Mid Glamorgan
* South Glamorgan
, Motto ...
. In the 12th century the castle began to be rebuilt in stone, probably by Robert of Gloucester, with a shell keep
A shell keep is a style of medieval fortification, best described as a stone structure circling the top of a motte.
In English castle morphology, shell keeps are perceived as the successors to motte-and-bailey castles, with the wooden fence arou ...
and substantial defensive walls being erected. Further work was conducted by the 6th Earl of Gloucester in the second half of the 13th century. Cardiff Castle was repeatedly involved in the conflicts between the Anglo-Normans and the Welsh, being attacked several times in the 12th century, and stormed in 1404 during the revolt of Owain Glyndŵr
Owain ap Gruffydd (), commonly known as Owain Glyndŵr or Glyn Dŵr (, anglicised as Owen Glendower), was a Welsh leader, soldier and military commander who led a 15 year long Welsh War of Independence with the aim of ending English rule in Wa ...
.
After being held by the de Clare and Despenser families for several centuries, the castle was acquired by The 13th Earl of Warwick and '' Comte de Aumale'' in 1423. Lord Warwick conducted extensive work on the castle, founding the main range on the west side of the castle, dominated by a tall octagonal tower. Following the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
, the status of the castle as a Marcher territory was revoked and its military significance began to decline. The Herbert family took over the property in 1550, remodelling parts of the main range and carrying out construction work in the outer bailey
An outer bailey or outer ward is the defended outer enclosure of a castle.Friar, Stephen (2003). ''The Sutton Companion to Castles'', Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2003, p. 22. It protects the inner bailey and usually contains those ancillary bui ...
, then occupied by Cardiff's Shire Hall and other buildings. During the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of re ...
Cardiff Castle was initially taken by a Parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democracy, democratic government, governance of a sovereign state, state (or subordinate entity) where the Executive (government), executive derives its democratic legitimacy ...
force, but was regained by Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governme ...
supporters in 1645. When fighting broke out again in 1648, a Royalist army attacked Cardiff in a bid to regain the castle, leading to the Battle of St Fagans
The Battle of St Fagans was a pitched battle during the Second English Civil War in 1648. A detachment from the New Model Army defeated an army of former Parliamentarian soldiers who had rebelled and were now fighting against Parliament.
B ...
just outside the city. Cardiff Castle escaped potential destruction
Destruction may refer to:
Concepts
* Destruktion, a term from the philosophy of Martin Heidegger
* Destructive narcissism, a pathological form of narcissism
* Self-destructive behaviour, a widely used phrase that ''conceptualises'' certain kin ...
by Parliament after the war and was instead garrisoned, probably to protect against a possible Scottish invasion.
In the mid-18th century, Cardiff Castle passed into the hands of the Stuart dynasty, Marquesses of Bute. John, 1st Marquess of Bute, employed Capability Brown and Henry Holland to renovate the main range, turning it into a Georgian mansion, and to landscape the castle grounds, demolishing many of the older medieval buildings and walls. During the first half of the 19th century the family became extremely wealthy as a result of the growth of the coal industry in Glamorgan. However, it was the 3rd Marquess of Bute who truly transformed the castle, using his vast wealth to back an extensive programme of renovations under William Burges
William Burges (; 2 December 1827 – 20 April 1881) was an English architect and designer. Among the greatest of the Victorian art-architects, he sought in his work to escape from both nineteenth-century industrialisation and the Neoc ...
. Burges remodelled the castle in a Gothic revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
style, lavishing money and attention on the main range. The resulting interior designs are considered to be amongst "the most magnificent that the gothic revival ever achieved". The grounds were re-landscaped and, following the discovery of the old Roman remains, reconstructed walls and a gatehouse in a Roman style were incorporated into the castle design. Extensive landscaped parks were built around the outside of the castle.
In the early 20th century, the 4th Marquess of Bute inherited the castle and construction work continued into the 1920s. The Bute lands and commercial interests around Cardiff were sold off or nationalised until, by the time of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, little was left except the castle. During the war, extensive air raid shelter
Air raid shelters are structures for the protection of non-combatants as well as combatants against enemy attacks from the air. They are similar to bunkers in many regards, although they are not designed to defend against ground attack (but many ...
s were built in the castle walls; they could hold up to 1,800 people. When the 4th Marquess died in 1947, the castle was given to the City of Cardiff. Today the castle is run as a tourist attraction, with the grounds housing the " Firing Line" regimental museum
In countries whose armies are organised on a regimental basis, such as the army of the United Kingdom, a regimental museum is a military museum dedicated to the history of a specific army regiment.
List of regimental museums in the UK
In addition ...
and interpretation centre. The castle has also served as a venue for events, including musical performances and festivals.
History
1st–4th centuries AD
The future site of Cardiff Castle was first used by the Romans as a defensive location for many years. The first fort was probably built about AD 55 and occupied until AD 80. It was a rectangular structure much larger than the current site, and formed part of the southern Roman border in Wales during the conquest of the Silures. When the border advanced, defences became less important and the fort was replaced with a sequence of two, much smaller, fortifications on the north side of the current site. A fourth fort was built in the middle of the 3rd century in order to combat the pirate threat along the coast, and forms the basis of the Roman remains seen on the castle site. The fort was almost square in design, approximately by large, constructed fromlimestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
brought by sea from Penarth
Penarth (, ) is a town and Community (Wales), community in the Vale of Glamorgan ( cy, Bro Morgannwg), Wales, exactly south of Cardiff city centre on the west shore of the Severn Estuary at the southern end of Cardiff Bay.
Penarth is a weal ...
. The fort's irregular shape was determined by the River Taff
The River Taff ( cy, Afon Taf) is a river in Wales. It rises as two rivers in the Brecon Beacons; the Taf Fechan (''little Taff'') and the Taf Fawr (''great Taff'') before becoming one just north of Merthyr Tydfil. Its confluence with the R ...
that flowed along the west side of the walls. The sea would have come much closer to the site than is the case in the 21st century, and the fort would have directly overlooked the harbour. This Roman fort was probably occupied at least until the end of the 4th century, but it is unclear when it was finally abandoned. There is no evidence for the re-occupation of the site until the 11th century.
11th century
 The
The Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Fran ...
began to make incursions into South Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards ...
from the late 1060s onwards, pushing westwards from their bases in recently occupied England. Their advance was marked by the construction of castles, frequently on old Roman sites, and the creation of regional lordships. The reuse of Roman sites produced considerable savings in the manpower required to construct large earth fortifications.
Cardiff Castle was built during this period. There are two possible dates for the construction: William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Norman ...
may have built a castle at Cardiff as early as 1081 on his return from his pilgrimage to St Davids
St Davids or St David's ( cy, Tyddewi, , "David's house”) is a city and a community (named St Davids and the Cathedral Close) with a cathedral in Pembrokeshire, Wales, lying on the River Alun. It is the resting place of Saint David, W ...
. Alternatively, the first Norman fortification may have been constructed around 1091 by Robert Fitzhamon
Robert Fitzhamon (died March 1107), or Robert FitzHamon (literally, 'Robert, son of Hamon'), Seigneur de Creully in the Calvados region and Torigny in the Manche region of Normandy, was the first Norman feudal baron of Gloucester and the Nor ...
, the lord of Gloucester. Fitzhamon invaded the region in 1090, and used the castle as a base for the occupation of the rest of southern Glamorgan
, HQ = Cardiff
, Government = Glamorgan County Council (1889–1974)
, Origin=
, Code = GLA
, CodeName = Chapman code
, Replace =
* West Glamorgan
* Mid Glamorgan
* South Glamorgan
, Motto ...
over the next few years. The site was close to the sea and could be easily supplied by ship, was well protected by the Rivers Taff and Rhymney and also controlled the old Roman road running along the coast.
Cardiff Castle was a motte-and-bailey
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy to ...
design. The old Roman walls had collapsed and the Normans used their remains as the basis for the outer castle perimeter, digging a defensive trench and throwing up a high bank of earth over the Roman fortifications. The Normans further divided the castle with an internal wall to form an inner and an outer bailey. In the north-west corner of the castle a wooden keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in c ...
was constructed on top of a tall earth motte, surrounded by a wide moat. The motte was the largest built in Wales. The overall area of the castle was around ; the inner bailey was around in area. Mills were essential to local communities during this period, and the castle mill was located outside the west side of the castle, fed by the River Taff; under local feudal law, the residents of Cardiff were required to use this mill to grind their own grain.
The conquered lands in Glamorgan were given out in packages called knights' fees, and many of these knights held their lands on condition that they provided forces to protect Cardiff Castle. Under this approach, called a castle-guard
Castle-guard was an arrangement under the feudal system, by which the duty of finding knights to guard royal castles was imposed on certain manors, knight's fees or baronies. The greater barons provided for the guard of their castles by exacting ...
system, some knights were required to maintain buildings called "houses" within the castle itself, in the outer bailey. Anglo-Saxon peasants settled the region around Cardiff, bringing with them English customs, although Welsh lords continued to rule the more remote districts almost independently until the 14th century. Cardiff Castle was a Marcher Lord
A Marcher lord () was a noble appointed by the king of England to guard the border (known as the Welsh Marches) between England and Wales.
A Marcher lord was the English equivalent of a margrave (in the Holy Roman Empire) or a marquis (in F ...
territory, enjoying special privileges and independence from the English Crown. The medieval town of Cardiff spread out from the south side of the castle.
12th–14th centuries
FitzHamon was fatally injured at theBattle of Tinchebray
The Battle of Tinchebray (alternative spellings: Tinchebrai or Tenchebrai) took place on 28 September 1106, in Tinchebray (today in the Orne ''département'' of France), Normandy, between an invading force led by King Henry I of England, and th ...
in 1106 and died shortly afterwards. Henry I Henry I may refer to:
876–1366
* Henry I the Fowler, King of Germany (876–936)
* Henry I, Duke of Bavaria (died 955)
* Henry I of Austria, Margrave of Austria (died 1018)
* Henry I of France (1008–1060)
* Henry I the Long, Margrave of the ...
then gave the castle in 1122 to Robert of Gloucester, the king's illegitimate son and the husband of FitzHamon's daughter, Mabe. After the failed attempt of Robert Curthose
Robert Curthose, or Robert II of Normandy ( 1051 – 3 February 1134, french: Robert Courteheuse / Robert II de Normandie), was the eldest son of William the Conqueror and succeeded his father as Duke of Normandy in 1087, reigning until 1106. ...
, duke of Normandy, William the Conqueror's eldest son, to take England from Henry I, the duke was moved here in 1126 from imprisonment at Devizes
Devizes is a market town and civil parish in Wiltshire, England. It developed around Devizes Castle, an 11th-century Norman architecture, Norman castle, and received a charter in 1141. The castle was besieged during the Anarchy, a 12th-century ...
and remained imprisoned in the castle until his death in 1134. Robert of Gloucester held the castle during the troubled years of the Anarchy
The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin, the only legiti ...
in England and Wales, and passed it on to his son, William Fitz Robert. Around the middle of the century, possibly under Robert of Gloucester, a wide, high shell keep
A shell keep is a style of medieval fortification, best described as a stone structure circling the top of a motte.
In English castle morphology, shell keeps are perceived as the successors to motte-and-bailey castles, with the wooden fence arou ...
was constructed on top of the motte, along with a stone wall around the south and west sides of the inner bailey. The polygonal shell keep has architectural links to a similar design at Arundel Castle. The building work was probably undertaken in response to the threat posed following the Welsh uprising of 1136.
Tensions with the Welsh continued, and in 1158 Ifor Bach
Ifor Bach (meaning Ivor the Short) (fl. 1158) also known as Ifor ap Meurig and in anglicised form Ivor Bach, Lord of Senghenydd, was a twelfth-century resident in and a leader of the Welsh in south Wales.
Welsh Lord of Senghenydd
At this perio ...
raided the castle and took William hostage for a period. A further attack followed in 1183. By 1184 town wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
s had been built around Cardiff, and the West Gate to the town was constructed in the gap between the castle and the river. William died in 1183, leaving three daughters. One of these, Isabel, Countess of Gloucester
Isabella, Countess of Gloucester (1173/1174 – 14 October 1217), was an English noblewoman who was married to King John prior to his accession.
Lineage
Isabella was the daughter of William Fitz Robert, 2nd Earl of Gloucester, and his wife Hawi ...
, was declared the sole heir to the estate by Henry II. This was contrary to legal custom in England, and was done in order that Henry could then marry her to his youngest son Prince John and thus provide him with extensive lands. John later divorced Isabel, but he retained control of the castle until she married Geoffrey de Mandeville in 1214.
 Upon Isabel's death in 1217 the castle passed through her sister to Gilbert de Clare, becoming part of the
Upon Isabel's death in 1217 the castle passed through her sister to Gilbert de Clare, becoming part of the Honour of Clare
Earl of Clare was a title of British nobility created three times: once each in the peerages of England, Great Britain and Ireland.
The title derives from Clare, Suffolk, where a prominent Anglo-Norman family was seated since the Norman Conque ...
, a major grouping of estates and fortifications in medieval England. The castle formed the centre of the family's power in South Wales, although the de Clares typically preferred to reside in their castles at Clare and Tonbridge
Tonbridge ( ) is a market town in Kent, England, on the River Medway, north of Royal Tunbridge Wells, south west of Maidstone and south east of London. In the administrative borough of Tonbridge and Malling, it had an estimated population ...
. Gilbert's son, Richard de Clare, 6th Earl of Gloucester
Richard de Clare, 5th Earl of Hertford, 6th Earl of Gloucester, 2nd Lord of Glamorgan, 8th Lord of Clare (4 August 1222 – 14 July 1262) was the son of Gilbert de Clare, 4th Earl of Hertford and Isabel Marshal.History of Tewkesbury by James Be ...
, carried out building work at the castle in the late 13th century, constructing the Black Tower that forms part of the southern gateway seen today. On the ground floor the tower contained the Stavell Oged and Stavell Wenn chambers, with three rooms constructed above them. Richard was also probably responsible for rebuilding the northern and eastern walls of the inner bailey in stone. The inner bailey was reached through a gatehouse on the eastern side, protected by two circular towers and later called the Exchequer Gate. The defensive work may have been prompted by the threat posed by the hostile Welsh leader Llywelyn ap Gruffudd
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd (c. 1223 – 11 December 1282), sometimes written as Llywelyn ap Gruffydd, also known as Llywelyn the Last ( cy, Llywelyn Ein Llyw Olaf, lit=Llywelyn, Our Last Leader), was the native Prince of Wales ( la, Princeps Wall ...
, Prince of Wales.
Richard's grandson, Gilbert de Clare, the last male de Clare, died at the Battle of Bannockburn
The Battle of Bannockburn ( gd, Blàr Allt nam Bànag or ) fought on June 23–24, 1314, was a victory of the army of King of Scots Robert the Bruce over the army of King Edward II of England in the First War of Scottish Independence. It was ...
in 1314 and the castle was given to Hugh Despenser the Younger
Hugh le Despenser, 1st Baron le Despenser (c. 1287/1289 – 24 November 1326), also referred to as "the Younger Despenser", was the son and heir of Hugh le Despenser, Earl of Winchester (the Elder Despenser), by his wife Isabella de Beaucham ...
, the controversial favourite of Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also called Edward of Caernarfon, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir apparent to t ...
. Poor harvests and harsh governance by the Despenser family encouraged a Welsh rebellion under Llywelyn Bren
Llywelyn Bren (), or Llywelyn ap Gruffudd ap Rhys / Llywelyn ap Rhys (also Llewelyn) or in en, Llywelyn of the Woods. He was a nobleman who led a 1316 revolt in Wales in the reign of King Edward II of England. It marked the last serious challen ...
in 1316; this was crushed and Llywelyn was hanged, drawn and quartered
To be hanged, drawn and quartered became a statutory penalty for men convicted of high treason in the Kingdom of England from 1352 under Edward III of England, King Edward III (1327–1377), although similar rituals are recorded during the rei ...
in Cardiff Castle in 1318 on Hugh's orders. The execution attracted much criticism from across both the English and Welsh communities, and in 1321 Hugh arrested Sir William Fleminge as a scapegoat for the incident, first detaining him in the Black Tower and then executing him in the castle grounds. Conflict between the Despensers and the other Marcher Lords broke out soon after, leading to the castle being sacked in 1321 during the Despenser War
The Despenser War (1321–22) was a baronial revolt against Edward II of England led by the Marcher Lords Roger Mortimer and Humphrey de Bohun. The rebellion was fuelled by opposition to Hugh Despenser the Younger, the royal favourite.Some his ...
. The Despensers recovered the castle and retained it for the rest of the century, despite the execution of Hugh Despenser for treason in 1326. Under a 1340 charter granted by the Despensers, the castle's constable
A constable is a person holding a particular office, most commonly in criminal law enforcement. The office of constable can vary significantly in different jurisdictions. A constable is commonly the rank of an officer within the police. Other peop ...
was made the ''de facto'' mayor of Cardiff, controlling the local courts.
15th–16th centuries
 By the 15th century, the Despensers were increasingly using Caerphilly Castle as their main residence in the region rather than Cardiff. Thomas le Despenser was executed in 1400 on charges of conspiring against Henry IV. In 1401 rebellion broke out in North Wales under the leadership of
By the 15th century, the Despensers were increasingly using Caerphilly Castle as their main residence in the region rather than Cardiff. Thomas le Despenser was executed in 1400 on charges of conspiring against Henry IV. In 1401 rebellion broke out in North Wales under the leadership of Owain Glyndŵr
Owain ap Gruffydd (), commonly known as Owain Glyndŵr or Glyn Dŵr (, anglicised as Owen Glendower), was a Welsh leader, soldier and military commander who led a 15 year long Welsh War of Independence with the aim of ending English rule in Wa ...
, quickly spreading across the rest of the country. In 1404 Cardiff and the castle were taken by the rebels, causing considerable damage to the Black Tower and the southern gatehouse in the process. On Thomas's death the castle passed first to his young son, Richard
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Frankish language, Old Frankish and is a Compound (linguistics), compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' an ...
, and on his death in 1414, through his daughter Isabel
Isabel is a female name of Spanish origin. Isabelle is a name that is similar, but it is of French origin. It originates as the medieval Spanish form of '' Elisabeth'' (ultimately Hebrew ''Elisheva''), Arising in the 12th century, it became popul ...
to the Beauchamp family. Isabel first married Richard de Beauchamp, the Earl of Worcester
Earl of Worcester is a title that has been created five times in the Peerage of England.
Five creations
The first creation came in 1138 in favour of the Norman noble Waleran de Beaumont. He was the son of Robert de Beaumont, 1st Earl of Leice ...
and then, on his death, to his cousin Richard de Beauchamp, the Earl of Warwick
Earl of Warwick is one of the most prestigious titles in the peerages of the United Kingdom. The title has been created four times in English history, and the name refers to Warwick Castle and the town of Warwick.
Overview
The first creation ...
, in 1423.
Richard did not acquire Caerphilly Castle as part of the marriage settlement, so he set about redeveloping Cardiff instead. He built a new tower alongside the Black Tower in 1430, restoring the gateway, and extended the motte defences. He also constructed a substantial new domestic range in the south-west of the site between 1425 and 1439, with a central octagonal tower high, sporting defensive machicolation
A machicolation (french: mâchicoulis) is a floor opening between the supporting corbels of a battlement, through which stones or other material, such as boiling water, hot sand, quicklime or boiling cooking oil, could be dropped on attackers at t ...
s, and featuring four smaller polygonal turrets facing the inner bailey. The range was built of Lias
Lias may refer to:
Geology
* Lias Formation, a geologic formation in France
*Lias Group, a lithostratigraphic unit in western Europe
* Early Jurassic, an epoch
People
* Godfrey Lias, British author
* Mohd Shamsudin Lias (born 1953), Malaysian ...
ashlar stone with limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
used for some of the details, set upon the spur bases characteristic of South Wales and incorporated parts of the older 4th and 13th century walls. The buildings were influenced by similar work in the previous century at Windsor Castle
Windsor Castle is a royal residence at Windsor in the English county of Berkshire. It is strongly associated with the English and succeeding British royal family, and embodies almost a millennium of architectural history.
The original c ...
and would in turn shape renovations at Newport and Nottingham Castle
Nottingham Castle is a Stuart Restoration-era ducal mansion in Nottingham, England, built on the site of a Norman castle built starting in 1068, and added to extensively through the medieval period, when it was an important royal fortress and o ...
s; the octagonal tower has architectural links to Guy's Tower, built at around the same time in Warwick Castle
Warwick Castle is a medieval castle developed from a wooden fort, originally built by William the Conqueror during 1068. Warwick is the county town of Warwickshire, England, situated on a meander of the River Avon. The original wooden motte-an ...
. A flower garden was built to the south of the range, with private access to Richard's chambers. Richard also rebuilt the town's wider defences, including a new stone bridge over the River Taff guarded by the West Gate, finishing the work by 1451.
 Cardiff Castle remained in the hands of Richard's son,
Cardiff Castle remained in the hands of Richard's son, Henry
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
* Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
and Henry's daughter, Anne
Anne, alternatively spelled Ann, is a form of the Latin female given name Anna. This in turn is a representation of the Hebrew Hannah, which means 'favour' or 'grace'. Related names include Annie.
Anne is sometimes used as a male name in the ...
until 1449. When Anne died, it passed by marriage to Richard Neville, who held it until his death in 1471 during the period of civil strife known as the Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
. As the conflict progressed and political fortunes rose and fell, the castle passed from George
George may refer to:
People
* George (given name)
* George (surname)
* George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George
* George Washington, First President of the United States
* George W. Bush, 43rd Presid ...
, the Duke of Clarence
Duke of Clarence is a substantive title which has been traditionally awarded to junior members of the British Royal Family. All three creations were in the Peerage of England.
The title was first granted to Lionel of Antwerp, the second son ...
, to Richard
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Frankish language, Old Frankish and is a Compound (linguistics), compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' an ...
, Duke of Gloucester, to Jasper Tudor
Jasper Tudor, Duke of Bedford (November 143121/26 December 1495), was the uncle of King Henry VII of England and a leading architect of his nephew's successful accession to the throne in 1485. He was from the noble Tudor family of Penmynydd i ...
, the Duke of Bedford
Duke of Bedford (named after Bedford, England) is a title that has been created six times (for five distinct people) in the Peerage of England. The first and second creations came in 1414 and 1433 respectively, in favour of Henry IV's third so ...
, back to Richard Neville's wife Anne
Anne, alternatively spelled Ann, is a form of the Latin female given name Anna. This in turn is a representation of the Hebrew Hannah, which means 'favour' or 'grace'. Related names include Annie.
Anne is sometimes used as a male name in the ...
, back to Jasper and finally to Prince Henry, the future Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
. The ascension of the Tudor dynasty
The House of Tudor was a royal house of largely Welsh and English origin that held the English throne from 1485 to 1603. They descended from the Tudors of Penmynydd and Catherine of France. Tudor monarchs ruled the Kingdom of England and it ...
to the English throne at the end of the wars heralded a change in the way Wales was administered. The Tudors were Welsh in origin, and their rule eased hostilities between the Welsh and English. As a result, defensive castles became less important. In 1495 Henry VII formally revoked the Marcher territory status of Cardiff Castle and the surrounding territories, bringing them under normal English law as the County of Glamorgan.
The Crown leased the castle to Charles Somerset in 1513; Charles used it while he was living in Cardiff. In 1550 William Herbert, later the Earl of Pembroke
Earl of Pembroke is a title in the Peerage of England that was first created in the 12th century by King Stephen of England. The title, which is associated with Pembroke, Pembrokeshire in West Wales, has been recreated ten times from its origin ...
, then bought Cardiff Castle and the surrounding estates from Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first E ...
. The outer bailey contained a range of buildings at this time, and extensive building work was carried out during the century. The Shire Hall had been built in the outer bailey, forming part of a walled complex of buildings that included the lodgings for the traditional twelve holders of castle-guard lands. The outer bailey also included orchards, gardens and a chapel. The castle continued to be used to detain criminals during the 16th century, with the Black Tower being used as a prison to hold them; the heretic Thomas Capper was burnt at the castle on the orders of Henry VIII. The visiting antiquarian
An antiquarian or antiquary () is an fan (person), aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient artifact (archaeology), artifac ...
John Leland described the keep as "a great thing and strong, but now in some ruine", but the Black Tower was considered to be in good repair. In the inner bailey, the Herberts built an Elizabethan extension to the north end of the main range, with large windows looking onto a new northern garden; the southern garden was replaced by a kitchen garden.
17th–18th centuries
 In 1610 the
In 1610 the cartographer
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an im ...
John Speed
John Speed (1551 or 1552 – 28 July 1629) was an English cartographer, chronologer and historian of Cheshire origins.S. Bendall, 'Speed, John (1551/2–1629), historian and cartographer', ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (OUP 2004/ ...
produced a map of the castle, and noted that it was "large and in good repair." In 1642, however, civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
broke out between the rival Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governme ...
supporters of King Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
and Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
. Cardiff Castle was then owned by Philip Herbert, a moderate Parliamentarian, and the castle was initially held by a pro-Royalist garrison. It was taken by Parliamentary forces in the early period of the war, according to popular tradition by a sneak attack using a secret passageway. The Royalist commander William Seymour, the Marquess of Hertford
The titles of Earl of Hertford and Marquess of Hertford have been created several times in the peerages of England and Great Britain.
The third Earldom of Hertford was created in 1559 for Edward Seymour, who was simultaneously created Baron Be ...
, then attacked the castle in turn, taking it in a surprise assault. Parliamentary forces and local troops then immediately besieged the castle, retaking it after five hours of fighting and reinstalling a garrison. In early 1645 Mr Carne, the High Sheriff, rebelled against Parliament, taking Cardiff town but initially failing to seize the castle. The King sent forces from Oxford, under the command of Sir Charles Kemys, to reinforce Carne but Parliament despatched a naval squadron to provide support to their forces from the sea. A small battle ensued before the castle was taken by the Royalists.
With the Royalist military position across the country worsening, King Charles himself came to Cardiff Castle that July to meet with local Welsh leaders. Relations between his commander in the region, Sir Charles Gerard, and the people of Glamorgan had deteriorated badly and when Charles left the castle, he was confronted by a small army of angry locals, demanding to be given control of the castle. These clubmen
Clubmen were bands of local defence vigilantes during the English Civil War (1642–1651) who tried to protect their localities against the excesses of the armies of both sides in the war. They sought to join together to prevent their wives and d ...
then declared themselves the "Peaceable Army" and increased their demands to include near independence for the region. After negotiations, a compromise was found in which the royal garrison would quit the castle, to be replaced by a local Glamorgan force, commanded by Sir Richard Beaupré; in return, £800 and a force of a thousand men were promised to Charles. In September, Charles returned to South Wales and reneged on the agreement, disbanding the Peaceable Army, but his military position in the region was collapsing. The Peaceable Army's leaders switched sides and forced the surrender of Cardiff and the castle to Parliament in mid-September.
With the outbreak of fresh fighting in 1648, a Royalist army of 8,000 fresh recruits was mustered under the command of General Rowland Laugharne
Major General Rowland Laugharne (1607 – 1675) was a member of the Welsh gentry, and a prominent soldier during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, in which he fought on both sides.
Laugharne began his career as a page to Robert Devereux, 3rd ...
and Sir Edward Stradling, with the intent of retaking Cardiff. Parliamentary forces in Brecon
Brecon (; cy, Aberhonddu; ), archaically known as Brecknock, is a market town in Powys, mid Wales. In 1841, it had a population of 5,701. The population in 2001 was 7,901, increasing to 8,250 at the 2011 census. Historically it was the coun ...
under the command of Colonel Thomas Horton moved quickly to reinforce the castle, although with only 3,000 men they were content to wait until a larger army under Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three Ki ...
could arrive from Gloucester
Gloucester ( ) is a cathedral city and the county town of Gloucestershire in the South West of England. Gloucester lies on the River Severn, between the Cotswolds to the east and the Forest of Dean to the west, east of Monmouth and east ...
. With time against them, the Royalist army attacked, leading to the battle of St Fagans
The Battle of St Fagans was a pitched battle during the Second English Civil War in 1648. A detachment from the New Model Army defeated an army of former Parliamentarian soldiers who had rebelled and were now fighting against Parliament.
B ...
just to the west of Cardiff, and a heavy Royalist defeat.
After the war, Cardiff Castle escaped the slighting
Slighting is the deliberate damage of high-status buildings to reduce their value as military, administrative or social structures. This destruction of property sometimes extended to the contents of buildings and the surrounding landscape. It is ...
, or deliberate damage and destruction, that affected many other castles. Probably because of the threat of a pro-Royalist invasion by the Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
Scots, a Parliamentary garrison was installed instead and the castle remained intact. The Herberts continued to own the castle as the Earls of Pembroke, both during the interregnum
An interregnum (plural interregna or interregnums) is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order. Archetypally, it was the period of time between the reign of one monarch and the next (coming from Latin '' ...
and after the restoration
Restoration is the act of restoring something to its original state and may refer to:
* Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage
** Audio restoration
** Film restoration
** Image restoration
** Textile restoration
* Restoration ecology
...
of Charles II. The castle's constable continued to act as mayor of the town of Cardiff, controlling the meetings of the town's burgesses, bailiffs and aldermen; the Herberts usually appointed members of the more important local gentry to this position during the period.
 Lady Charlotte Herbert was the last of the family to control Cardiff Castle. She married twice, latterly to Thomas, Viscount Windsor, and on her death in 1733 the castle passed to their son,
Lady Charlotte Herbert was the last of the family to control Cardiff Castle. She married twice, latterly to Thomas, Viscount Windsor, and on her death in 1733 the castle passed to their son, Herbert
Herbert may refer to:
People Individuals
* Herbert (musician), a pseudonym of Matthew Herbert
Name
* Herbert (given name)
* Herbert (surname)
Places Antarctica
* Herbert Mountains, Coats Land
* Herbert Sound, Graham Land
Australia
* Herbert ...
. Herbert's daughter, Charlotte Jane Windsor, married, in November 1766, John, Lord Mount Stuart, who rose to become the Marquess of Bute in 1794, beginning a family line that would control the castle for the next century.
In 1776, Lord Mount Stuart (later created The 1st Marquess of Bute in 1794) began to renovate the property with the intention of turning it into a residence for his son, John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
. The grounds were radically altered under a programme of work that involved Capability Brown and his son-in-law, Henry Holland. The stone wall that separated the inner and outer baileys was destroyed using gunpowder, the Shire Hall and the knights' houses in the outer bailey were destroyed and the remaining ground partially flattened; the whole of the area was laid with turf. Considerable work was carried out on the main lodgings, demolishing the Herbert additions, building two new wings and removing many of the older features to produce a more contemporary, 18th-century appearance. The keep and motte was stripped of the ivy and trees that had grown up them, and a spiral path was laid down around the motte. The motte's moat was filled in as part of the landscaping. A summer house was built in the south-east corner of the castle. Further work was planned on the property, including a reported proposal to roof the keep in copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, insert new windows and turn it into an assembly room for dances, but these projects were cut short by the (by now) Marquess's son's death in 1794.
19th century
In 1814 Lord Bute's grandson,John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
, inherited his title and the castle. In 1825 the new Marquess began a sequence of investments in the Cardiff Docks
Cardiff Docks ( cy, Dociau Caerdydd) is a port in southern Cardiff, Wales. At its peak, the port was one of the largest dock systems in the world with a total quayage of almost . Once the main port for the export of South Wales coal, the Port ...
, an expensive programme of work that would enable Cardiff to become a major coal exporting port. Although the Docks were not particularly profitable, they transformed the value of the Butes' mining and land interests, making the family immensely wealthy. By 1900, the family estate owned of land in Glamorgan.
The second Marquess preferred to live on the Isle of Bute
The Isle of Bute ( sco, Buit; gd, Eilean Bhòid or '), known as Bute (), is an island in the Firth of Clyde in Scotland, United Kingdom. It is divided into highland and lowland areas by the Highland Boundary Fault.
Formerly a constituent is ...
in Scotland and only used Cardiff Castle occasionally. The castle saw little investment and only four full-time servants were maintained on the premises, meaning that cooked food had to be brought across from the kitchens at a nearby hotel. The castle remained at the centre of the Butes' political power base in Cardiff, however, with their faction sometimes termed as "the Castle party". During the violent protests of the Merthyr Rising
The Merthyr Rising, also referred to as the Merthyr Riots, of 1831 was the violent climax to many years of simmering unrest among the large working class population of Merthyr Tydfil in Wales and the surrounding area. The Rising marked the fi ...
of 1831, the Marquess-based himself at Cardiff Castle, from where he directed operations and kept Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A roads in Zone 3 of the Great Britain numbering scheme, A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea, London, Chelsea. It is the main ...
informed of the unfolding events. The governance of the then town of Cardiff was finally reformed by an Act of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the Legislature, legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of ...
in 1835, introducing a town council and a mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well a ...
, severing the link with the castle constable.
John, 3rd Marquess of Bute, inherited the title and castle in 1848. He was then less than a year old, and as he grew up he came to despise the existing castle, believing that it represented a mediocre, half-hearted example of the Gothic style. The young Lord Bute engaged the architect William Burges
William Burges (; 2 December 1827 – 20 April 1881) was an English architect and designer. Among the greatest of the Victorian art-architects, he sought in his work to escape from both nineteenth-century industrialisation and the Neoc ...
to undertake the remodelling of the castle. The two shared a passion in medieval Gothic Revivalism and this, combined with Bute's huge financial resources, enabled Burges to rebuild the property on a grand scale. Burges brought with him almost of all of the team that had supported him on earlier projects, including John Starling Chapple
John Starling Chapple (1840–1922) was a stonemason and architect who worked as office manager for William Burges.
Born in Exeter, the son of a carpenter, he moved to London and worked with Burges from the 1850s until the latter's death in 188 ...
, William Frame
William Frame was an English architect.
Life and works
Frame was born at Melksham, Wiltshire in 1848. Training as an architect, he was articled firstly to William Smith of Trowbridge, he then became assistant to John Prichard of Llandaff. In 1 ...
and Horatio Lonsdale. Burges's contribution, in particular his research into the history of the castle and his architectural imagination, was critical to the transformation.
 Work began on Lord Bute's coming of age in 1868 with the construction of the high Clock Tower. The tower, built in Burges's signature
Work began on Lord Bute's coming of age in 1868 with the construction of the high Clock Tower. The tower, built in Burges's signature Forest of Dean
The Forest of Dean is a geographical, historical and cultural region in the western part of the county of Gloucestershire, England. It forms a roughly triangular plateau bounded by the River Wye to the west and northwest, Herefordshire to the n ...
ashlar
Ashlar () is finely dressed (cut, worked) stone, either an individual stone that has been worked until squared, or a structure built from such stones. Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, generally rectangular cuboid, mentioned by Vitruv ...
stone, formed a suite of bachelor's rooms, comprising a bedroom, a servant's room and the Summer and Winter smoking rooms. Externally, the tower was a re-working of a design Burges had previously used in an unsuccessful competition entry for the Royal Courts of Justice
The Royal Courts of Justice, commonly called the Law Courts, is a court building in Westminster which houses the High Court and Court of Appeal of England and Wales. The High Court also sits on circuit and in other major cities. Designed by Ge ...
in London. Internally, the rooms were sumptuously decorated with gildings, carvings and cartoons, many allegorical in style, depicting the seasons, myths and fables. In his ''A History of the Gothic Revival'', written as the tower was being built, Charles Locke Eastlake wrote of Burges's "peculiar talents (and) luxuriant fancy." The Summer Smoking Room rested at the top of the structure and was two storeys high with an internal balcony that, through an unbroken band of windows, gave views of the Cardiff Docks, the Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel ( cy, Môr Hafren, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River Seve ...
, and the Glamorgan countryside. The floor had a map of the world in mosaic. The sculpture was created by Thomas Nicholls.
As the rest of the castle was developed, work progressed along the rest of the 18th century range including the construction of the Guest Tower, the Arab Room, the Chaucer Room, the Nursery, the Library, the Banqueting Hall and bedrooms for both Lord and Lady Bute. In plan, the new castle followed the arrangement of a standard Victorian country house quite closely. The Bute Tower included Lord Bute's bedroom and ended in another highlight, the Roof Garden, featuring a sculpture of the Madonna and child
In art, a Madonna () is a representation of Mary, either alone or with her child Jesus. These images are central icons for both the Catholic and Orthodox churches. The word is (archaic). The Madonna and Child type is very prevalent in ...
by Ceccardo Fucigna. Bute's bedroom contained extensive religious iconography and an en-suite bathroom. The Octagon Tower followed, including an oratory, built on the spot where Bute's father died, and the Chaucer Room, the roof of which is considered by historian Mark Girouard to be a "superb example of Burges's genius".
 The central part of the castle comprised a two-storey banqueting hall, with the library below. Both are enormous, the latter to hold part of the bibliophile Marquess's vast library. Both included elaborate carvings and fireplaces, those in the banqueting hall depicting the castle itself in the time of Robert, Duke of Normandy. The decoration here is less impressive than elsewhere in the castle, as much of it was completed after Burges's death by Lonsdale, a less talented painter. The Arab Room in the Herbert Tower remains however one of Burges's masterpieces. Its jelly mould ceiling in a Moorish style is particularly notable. It was this room on which Burges was working when he died and Bute placed Burges's initials, and his own, and the date 1881 in the fireplace as a memorial. The central portion of the castle also included the Grand Staircase, recorded in a watercolour perspective prepared by
The central part of the castle comprised a two-storey banqueting hall, with the library below. Both are enormous, the latter to hold part of the bibliophile Marquess's vast library. Both included elaborate carvings and fireplaces, those in the banqueting hall depicting the castle itself in the time of Robert, Duke of Normandy. The decoration here is less impressive than elsewhere in the castle, as much of it was completed after Burges's death by Lonsdale, a less talented painter. The Arab Room in the Herbert Tower remains however one of Burges's masterpieces. Its jelly mould ceiling in a Moorish style is particularly notable. It was this room on which Burges was working when he died and Bute placed Burges's initials, and his own, and the date 1881 in the fireplace as a memorial. The central portion of the castle also included the Grand Staircase, recorded in a watercolour perspective prepared by Axel Haig
Axel Herman Haig ( sv, Axel Herman Hägg); (10 November 1835 –August 23, 1921) was a Swedish-born artist, illustrator and architect. His paintings, illustrations and etchings, undertaken for himself and on behalf of many of the foremost architect ...
.
Burges's interiors at Cardiff Castle have been widely praised. The historian Megan Aldrich considers them amongst "the most magnificent that the gothic revival ever achieved", J. Mordaunt Crook
Joseph Mordaunt Crook, (born 27 February 1937), generally known as J. Mordaunt Crook, is an English architectural historian and specialist on the Georgian and Victorian periods. He is an authority on the life and work of the Victorian architec ...
has described them as "three dimensional passports to fairy kingdoms and realms of gold", and John Newman praises them as "most successful of all the fantasy castles of the nineteenth century." The exterior of the castle, however, has received a more mixed reception from critics. Crook admires the variegated and romantic silhouette of the building, but architect John Grant considered them to present a "picturesque if not happy combination" of varying historical styles, and Adrian Pettifer criticises them as "incongruous" and excessively Gothic in style.
Work was also carried out on the castle grounds, the interior being flattened further, destroying much of the medieval and Roman archaeological remains. In 1889, Lord Bute's building works uncovered the remains of the old Roman fort for the first time since the 11th century, leading to archaeological investigations being carried out in 1890. New walls in a Roman style were built by William Frame
William Frame was an English architect.
Life and works
Frame was born at Melksham, Wiltshire in 1848. Training as an architect, he was articled firstly to William Smith of Trowbridge, he then became assistant to John Prichard of Llandaff. In 1 ...
on the foundations of the originals, complete with a reconstructed Roman North Gate, and the outer medieval bank was stripped away around the new walls.
The grounds were extensively planted with trees and shrubs, including over the motte. From the late 18th century until the 1850s the castle grounds were completely open to the public, but restrictions were imposed in 1858 and as a replacement the 434 acres of land to the west and north of the castle was turned into Bute Park
Bute Park and Arboretum () is a park in Cardiff, Wales. It comprises of landscaped gardens and parkland that once formed the grounds of Cardiff Castle. The park is named after the 3rd Marquess of Bute, whose family owned the castle.
History and ...
. From 1868, the castle grounds were closed to the public altogether. Stables were built just to the north of the castle, but only half were completed during the 19th century. The Animal Wall
The Animal Wall ( cy, Wal yr Anifeiliaid) is a sculptured wall depicting 15 animals in the Castle Quarter of the city centre of Cardiff, Wales. It stands to the west of the entrance to Cardiff Castle, having been moved from its original position ...
was built along the south side of the castle, decorated with statues of animals, and the Swiss Bridge – a combination of summerhouse and river-crossing – was erected over the river by the West Gate. Cathays Park was built on the east side of the castle, but was sold to the city of Cardiff in 1898.
20th and 21st centuries

John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
, the fourth Marquess, acquired the castle in 1900 on the death of his father, and the family estates and investments around the castle began to rapidly reduce in size. Cardiff had grown hugely in the previous century, its population increasing from 1,870 in 1800 to around 250,000 in 1900, but the coal trade began to diminish after 1918 and industry suffered during the depression of the 1920s. John only inherited a part of the Butes' Glamorgan estates, and in the first decades of the 20th century he sold off much of the remaining assets around Cardiff, including the coal mines, docks and railway companies, with the bulk of the land interests being finally sold off or nationalised in 1938.
Development work on the castle continued. There was extensive restoration of the medieval masonry in 1921, with architect John Grant rebuilding the South Gate and the barbican tower, and reconstructing the medieval West Gate and town wall alongside the castle, with the Swiss Bridge being moved in 1927 to make room for the new West Gate development. Further archaeological investigations were carried out into the Roman walls in 1922 and 1923, leading to Grant redesigning the northern Roman gatehouse. The second half of the castle stables were finally completed. The Animal Wall was moved in the 1920s to the west side of the castle to enclose a pre-Raphaelite
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood (later known as the Pre-Raphaelites) was a group of English painters, poets, and art critics, founded in 1848 by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, William Michael Rossetti, James ...
themed garden. The grand staircase in the main range was torn out in the 1930s. During World War II, extensive tunnels within the medieval walls were used as air-raid shelter
Air raid shelters are structures for the protection of non-combatants as well as combatants against enemy attacks from the air. They are similar to bunkers in many regards, although they are not designed to defend against ground attack (but many ...
s, with eight different sections, able to hold up to 1,800 people in total, and the castle was also used to tether barrage balloon
A barrage balloon is a large uncrewed tethered balloon used to defend ground targets against aircraft attack, by raising aloft steel cables which pose a severe collision risk to aircraft, making the attacker's approach more difficult. Early barra ...
s above the city.
In 1947, John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
, the fifth Marquess, inherited the castle on the death of his father and faced considerable death duties
An inheritance tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property of a person who has died, whereas an estate tax is a levy on the estate (money and property) of a person who has died.
International tax law distinguishes between an es ...
. He sold the very last of the Bute lands in Cardiff and gave the castle and the surrounding park to the city on behalf of the people of Cardiff; the family flag was taken down from the castle as part of the official hand-over ceremony. The castle was protected as a grade I
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
and as a scheduled monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage and d ...
.
Cardiff Castle is now run as a tourist attraction, and is one of the most popular sites in the city. The castle is not fully furnished, as the furniture and fittings in the castle were removed by the Marquess in 1947 and subsequently disposed of; an extensive restoration has been carried out, however, of the fittings originally designed for the Clock Tower by Burges. The Royal Welsh College of Music and Drama
, image_name = Royal Welsh College of Music & Drama.jpg
, image_size =
, motto =
, established = 1949
, type = Public
, staff =
, vice_chancellor =
, students = 779 (2017/18)
, undergrad ...
, founded in 1949, was housed in the castle's main range for many years, but moved into the castle's former stables north of the castle in 1998. A new interpretation centre, which opened in 2008, was built alongside the South Gate at a cost of £6 million, and the castle also contains " Firing Line", the joint regimental museum
In countries whose armies are organised on a regimental basis, such as the army of the United Kingdom, a regimental museum is a military museum dedicated to the history of a specific army regiment.
List of regimental museums in the UK
In addition ...
of the 1st The Queen's Dragoon Guards and the Royal Welsh
The Royal Welsh (R WELSH) ( cy, Y Cymry Brenhinol) is an armoured infantry regiment of the British Army. It was established in 2006 from the Royal Welch Fusiliers (23rd Foot) and the Royal Regiment of Wales (24th/41st Foot).
History
The ...
.
The castle has been used for a range of cultural and social events. The castle has seen various musical performances, including by Tom Jones, Green Day
Green Day is an American rock band formed in the East Bay of California in 1987 by lead vocalist and guitarist Billie Joe Armstrong, together with bassist and backing vocalist Mike Dirnt. For most of the band's career, they have been a powe ...
and the Stereophonics, with a capacity to accommodate over 10,000 people. During the 1960s and 1970s the castle was the setting for a sequence of military tattoo
A military tattoo is a performance of music or display of armed forces in general. The term comes from the early 17th-century Dutch phrase ''doe den tap toe'' ("turn off the tap"), a signal sounded by drummers or trumpeters to instruct innkeeper ...
s.
See also
*List of castles in Wales
Wales is sometimes called the "castle capital of the world" because of the large number of castles in a relatively small area. Wales had about 600 castles, of which over 100 are still standing, either as ruins or as restored buildings. The ...
* Castles in Great Britain and Ireland
Castles have played an important military, economic and social role in Great Britain and Ireland since their introduction following the Norman invasion of England in 1066. Although a small number of castles had been built in England in the 1050 ...
* Grade I listed buildings in Cardiff
There are around 1,000 listed buildings in Cardiff, the capital city of Wales. A listed building is one considered to be of special architectural, historical or cultural significance, which is protected from being demolished, extended or alter ...
* List of tallest buildings in Cardiff
This is a list of the tallest buildings in Cardiff that are in height and above in the capital of Wales. They include buildings ranging from the ornate civic centre to the historic Cardiff Castle and Llandaff Cathedral.
The city's growth is ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
Cardiff Castle's official website
{{Authority control Economy of Cardiff Castles in Cardiff Grade I listed buildings in Cardiff Grade I listed castles in Wales Mock castles in Wales
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
Scheduled monuments in Cardiff
William Burges buildings
Gothic Revival architecture in Wales
Towers in Wales
Museums in Cardiff
Historic house museums in Wales
Landmarks in Cardiff
Gardens by Capability Brown
Motte-and-bailey castles
Moorish Revival architecture in the United Kingdom
Music venues in Cardiff
Castle, Cardiff
Register of Parks and Gardens of Special Historic Interest in Wales